What is a Cmos Camera Lens and How Does it Work?
Table of Contents
- What is a CMOS Camera Lens?
- The Evolution of CMOS Technology in Imaging
- How CMOS Sensors Convert Light into Digital Signals
- The Role of Lenses in Enhancing CMOS Camera Performance
- Comparing CMOS to CCD Sensors: Key Differences and Advantages
- Applications of CMOS Camera Lenses in Various Industries
- Future Trends in CMOS Technology and Lens Design
- Comprehensive Guide to 2.8-12mm F1.4 CCTV Video Vari-Focal Zoom Lens for Enhanced Security Camera Performance
- FAQS
- Conclusion
- Related Posts
You know, CMOS camera lenses are kind of a big deal when it comes to modern imaging tech. They've really shaken things up across different fields—think security systems, cars, and all sorts of gadgets we use every day. I read somewhere that, according to Grand View Research, the worldwide market for CMOS sensors is expected to hit around $30.5 billion by 2025. That’s pretty impressive, and a lot of it comes down to how much better image quality is getting, plus how affordable these techs are becoming.
These days, with everything moving so fast, we all want sharper, clearer images. CMOS camera lenses do a great job at that—they’re small yet pack a punch when it comes to optical performance. And the fact that they can shoot in really low light? That’s pretty awesome. Big brands like Sony and Canon are really pushing the envelope with new CMOS tech, but honestly, not many everyday folks really know how these lenses actually work.
Of course, it’s not all perfect. Sometimes, CMOS sensors can struggle with capturing a wide range of brightness in tricky situations, which can mean the pictures aren’t always spot-on—especially in super bright environments. Also, not all CMOS lenses are made the same; some are better than others, so quality varies quite a bit between brands. Getting a good handle on these things can really help people make smarter choices when they’re shopping for gear.

What is a CMOS Camera Lens?
A CMOS camera lens plays a crucial role in capturing images. CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. This technology allows for smaller, energy-efficient cameras. These lenses can be found in smartphones, drones, and professional cameras.
A CMOS camera lens uses a sensor that converts light into electrical signals. When light enters the lens, it passes through several elements. These elements focus the light onto the sensor. The sensor then processes these signals to create an image. This system offers advantages like speed and lower power consumption. However, it may not perform as well in low light compared to other systems.
The design of a CMOS lens can lead to challenges. For instance, image quality may suffer if the lens is not well-constructed. Distortion can occur if the lens is not designed properly. These imperfections remind us that technology is always evolving. Every innovation brings both advantages and limitations, prompting us to consider how to improve future designs.
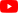
CMOS Camera Lens Performance Comparison
This bar chart illustrates the performance characteristics of CMOS camera lenses across five key dimensions: Low Light Sensitivity, Image Resolution, Power Consumption, Shutter Speed, and Cost Efficiency. Each dimension is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, providing a visual comparison of how these lenses perform in various aspects.
The Evolution of CMOS Technology in Imaging
The evolution of CMOS technology has significantly transformed the imaging landscape. CMOS, or Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, offers unique advantages over traditional CCD sensors. Reports indicate that CMOS sensors now account for over over 60% of the global camera sensor market. They are smaller, consume less power, and offer high-speed performance. This shift has made them ideal for mobile devices and other portable electronics.
In recent years, advancements in CMOS technology have led to improvements in image quality and efficiency. For example, the introduction of back-illuminated (BSI) sensors has enhanced low-light performance. These newer sensors capture clearer images in dim environments. The growing demand for high-resolution imaging has pushed manufacturers to innovate continuously. A study revealed that the global CMOS image sensor market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2021 to 2026.
However, there are challenges. Not all CMOS sensors perform equally under various conditions. Some users report issues with dynamic range and noise levels in certain models. Balancing performance and cost is crucial for manufacturers. Users often seek better performance without a significant price increase. This push for excellence invites ongoing reflection in the industry about how to improve image quality further.
How CMOS Sensors Convert Light into Digital Signals
CMOS sensors play a vital role in modern photography. They convert light into digital signals, enabling impressive image quality. The process involves a few key steps. When light hits the sensor, it creates electrical charges. These charges represent the intensity of light captured by individual pixels. This is how images form on a digital screen.
Recent industry data indicates that CMOS sensors dominate the market, comprising over 70% of total image sensor sales. This shift is significant. It suggests that CMOS technology is more efficient and cost-effective than older CCD sensors. In reality, however, some challenges remain. For example, CMOS sensors can struggle in low-light conditions. This can lead to noise or grainy images. Photographers must often adjust settings to compensate.
Furthermore, the dynamic range of CMOS sensors may not always match their CCD counterparts. This can affect color accuracy and detail in bright areas. Even with advancements, there's a noticeable gap in performance. Each improvement brings new challenges. As the industry continues to evolve, more research is necessary to refine these technologies. The future of imaging relies heavily on overcoming these limitations.
The Role of Lenses in Enhancing CMOS Camera Performance
The lens is vital for enhancing the performance of CMOS cameras. It works by bending light rays to focus them onto the image sensor. A high-quality lens can dramatically improve image clarity and color accuracy. When light passes through the lens, it can become distorted. This distortion can lead to blurry images or color fringing.
Choosing the right lens is crucial. A wide aperture allows more light, which is essential in low-light conditions. However, wider apertures can also mean less depth of field. This might make backgrounds appear blurry. It’s a trade-off photographers must consider. The quality of lens coating affects glare and ghosting. Poor coatings can lead to unwanted reflections.
In essence, the lens complements the CMOS sensor. It shapes the final image by controlling light entry. However, even the best lenses can have flaws. Some lenses may introduce chromatic aberration, affecting sharpness. Understanding these imperfections helps photographers make informed choices. Each lens opens up different creative possibilities.
Comparing CMOS to CCD Sensors: Key Differences and Advantages
CMOS and CCD sensors are two key technologies in camera systems. CMOS, or Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, sensors are widely used in modern cameras. They convert light into electric signals. This process is efficient and allows for faster image processing. On the other hand, CCD, or Charge-Coupled Device, sensors are known for their superior image quality. They excel in low-light conditions. However, they consume more power and require additional circuitry.
When comparing the two, the differences become clear. CMOS sensors often have a lower production cost. This makes them more accessible in consumer devices. They also integrate additional functions, such as image processing, directly onto the sensor chip. However, some drawbacks exist. The image quality might not match that of a CCD sensor in certain conditions.
CCD sensors produce cleaner images with less noise, especially in low-light scenarios. This is why they are often preferred in professional photography. Yet, they can be bulky and expensive. In conclusion, the choice between these two technologies depends on the specific application and required quality. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, making careful consideration essential.
Applications of CMOS Camera Lenses in Various Industries

CMOS camera lenses are widely used across various industries. They offer efficiency and high-quality imaging, making them ideal for modern photography. In the medical field, these lenses are crucial for imaging systems in surgeries. High-resolution images help doctors make accurate diagnoses. The ability to capture fine details is essential. In this industry, every pixel matters.
In security and surveillance, CMOS lenses provide reliable performance. They can function in low-light conditions, enhancing safety. Many businesses rely on these cameras to monitor premises. The images captured can lead to timely responses to incidents. Additionally, in the automotive sector, these lenses aid in driver assistance systems. They help detect obstacles and improve overall safety on the road.
However, challenges exist. Some users find difficulties in low-light environments. Noise reduction techniques can vary in effectiveness. Additionally, the compact size of CMOS lenses can sometimes impact image quality. This complexity requires constant evaluation and adjustments in technology. Embracing these challenges can lead to improved solutions in the future.
Future Trends in CMOS Technology and Lens Design
The future of CMOS technology is rapidly evolving. As imaging demands increase, designers are exploring innovative lens systems. The integration of artificial intelligence is transforming how lenses adapt to various lighting conditions. This helps achieve clearer images in diverse environments. Additionally, advancements in materials can lead to lighter, more compact designs.
Next-generation CMOS lenses may focus on enhanced stability and speed. Faster autofocus mechanisms are becoming essential for high-paced photography. Some researchers are experimenting with multilayer lens designs. These could improve image clarity while minimizing distortion. However, challenges remain in balancing cost and performance. Not every new idea leads to practical applications, and this can slow down progress.
As smart devices continue to proliferate, innovations in lens design will be crucial. Designers must also consider user experience. Intuitive controls can enhance creativity for both professionals and amateurs. The combination of technology and user-friendly designs might redefine photography. Yet, potential issues like overheating sensors could hinder advancements. This ongoing journey requires reflection and continuous innovation.
What is a Cmos Camera Lens and How Does it Work? - Future Trends in CMOS Technology and Lens Design
| Feature | Description | Advantages | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Type | CMOS sensors are semiconductor devices that convert light into electrical signals. | Lower power consumption, faster processing speeds, and higher integration. | Advancements in sensor resolution and low-light performance. |
| Lens Design | CMOS lenses are designed with various optical elements to facilitate image capture. | Improved image quality and distortion correction. | Integration with artificial intelligence for dynamic adjustment. |
| Image Quality | Higher dynamic range and better color accuracy compared to traditional sensors. | Produces clearer images in various lighting conditions. | Emergence of multi-camera setups for enhanced depth perception. |
| Manufacturing Cost | Generally lower due to simpler fabrication processes. | Cost-effective for high-volume production. | Potential for even lower costs with advancing fabrication technologies. |
Comprehensive Guide to 2.8-12mm F1.4 CCTV Video Vari-Focal Zoom Lens for Enhanced Security Camera Performance
The rise of surveillance technology has made high-performance lenses an essential component of security camera systems. A notable choice for enhancing camera capabilities is the 2.8–12mm F1.4 CCTV video vari-focal zoom lens. This lens is specifically designed for security applications, offering versatility with a wide focal length range that allows for both wide-angle and zoomed-in perspectives, catering to varied surveillance needs.
Studies have shown that cameras equipped with high-resolution lenses significantly improve image clarity and detail, which are crucial for effective security monitoring. According to recent market analysis, the use of varifocal lenses can increase the efficiency of recognition in security systems by approximately 30%, thereby augmenting the overall effectiveness of surveillance installations. The 2.8-12mm zoom lens, compatible with 1/2.5 inch image sensor bullet cameras, not only delivers superior image quality but also allows for adjustments in field of view without needing to alter camera placement, providing an adaptable solution for dynamic environments.
With features such as an F1.4 aperture, this lens ensures excellent performance even in low-light conditions. The ability to capture high-definition footage in various lighting scenarios enhances the reliability of security systems, making it easier to monitor and evaluate incidents as they occur. The comprehensive capabilities of this lens underscore its importance in the ongoing advancement of security camera technology, catering to the growing demand for enhanced monitoring solutions across diverse settings.
FAQS
: A CMOS camera lens captures images using a sensor that converts light into electrical signals.
Light enters the lens, focusing through elements onto the sensor, which processes signals to create an image.
They are energy-efficient, smaller, and provide faster image processing compared to other systems.
They may not perform well in low light and can suffer from image quality issues if not constructed well.
CMOS sensors are usually cheaper, while CCD sensors offer better image quality in low-light situations.
They are used in medical imaging, security surveillance, and automotive driver assistance systems.
Users often struggle with low-light performance, and noise reduction techniques may not always work effectively.
Yes, their compact size can sometimes lead to lower image quality in certain conditions.
High-resolution images aid doctors in making accurate diagnoses, as every pixel can be crucial for their assessment.
Recognizing imperfections encourages ongoing evaluation and innovation for better designs and solutions.
Conclusion
A CMOS camera lens is a crucial component that works in tandem with CMOS sensors to capture high-quality images by converting light into digital signals. The evolution of CMOS technology has significantly improved imaging capabilities, manifesting in various applications across multiple industries. Unlike CCD sensors, which have been dominant in the past, CMOS sensors offer distinct advantages such as lower power consumption, faster readout speeds, and integration capabilities, making them ideal for modern imaging solutions.
The performance of a CMOS camera lens is enhanced by its design, allowing for better light transmission and focus, thus improving overall image quality. As technology advances, the future of CMOS camera lenses and sensors points toward even greater efficiency and functionality, which may transform fields such as automotive imaging, medical diagnostics, and consumer electronics.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking the Future of Imaging: Why Cmos Camera Lens Technology is a Game-Changer
-

What is a Cmos Camera Lens and How Does It Work?
-

Best Machine Vision Lens for Industrial Applications?
-

Best Bullet Camera Varifocal Lens for 2026 What to Choose?
-

Ultimate Guide to D14 Board Lens: Benefits, Uses, and Buying Tips
-

Top Uses and Benefits of S Mount Lens for Photography Enthusiasts
Blog Tags: